| ( ! ) Warning: Undefined array key "blockId" in /home/kbxmjwdb/public_html/wp-content/plugins/table-of-contents-block/table-of-contents-block.php on line 159 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Call Stack | ||||
| # | Time | Memory | Function | Location |
| 1 | 0.0001 | 353960 | {main}( ) | .../index.php:0 |
| 2 | 0.0001 | 354320 | require( '/home/kbxmjwdb/public_html/wp-blog-header.php ) | .../index.php:17 |
| 3 | 0.1227 | 10550592 | require_once( '/home/kbxmjwdb/public_html/wp-includes/template-loader.php ) | .../wp-blog-header.php:19 |
| 4 | 0.1742 | 18262296 | include( '/home/kbxmjwdb/public_html/wp-content/themes/generatepress/single.php ) | .../template-loader.php:106 |
| 5 | 0.2512 | 19770176 | generate_do_template_part( $template = 'single' ) | .../single.php:29 |
| 6 | 0.2512 | 19770176 | get_template_part( $slug = 'content', $name = 'single', $args = ??? ) | .../theme-functions.php:568 |
| 7 | 0.2512 | 19770696 | locate_template( $template_names = [0 => 'content-single.php', 1 => 'content.php'], $load = TRUE, $load_once = FALSE, $args = [] ) | .../general-template.php:206 |
| 8 | 0.2512 | 19770808 | load_template( $_template_file = '/home/kbxmjwdb/public_html/wp-content/themes/generatepress/content-single.php', $load_once = FALSE, $args = [] ) | .../template.php:745 |
| 9 | 0.2512 | 19771224 | require( '/home/kbxmjwdb/public_html/wp-content/themes/generatepress/content-single.php ) | .../template.php:812 |
| 10 | 0.2525 | 19818952 | the_content( $more_link_text = ???, $strip_teaser = ??? ) | .../content-single.php:73 |
| 11 | 0.2526 | 19818952 | apply_filters( $hook_name = 'the_content', $value = '<!-- wp:paragraph -->\n<p><strong>NCERT solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 – Why Do We Fall Ill? (Updated)</strong></p>\n<!-- /wp:paragraph -->\n\n<!-- wp:table-of-contents-block/table-of-contents-block {"headers":[{"level":3,"content":"\\u003cstrong\\u003eNCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science – Page 178:\\u003c/strong\\u003e","text":"NCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science – Page 178:","link":"ncert-textbook-for-class-9-science-page-178"},{"level":3,"content":"In-Text Questions 13.2.5","text":"In-Text Questio'... ) | .../post-template.php:256 |
| 12 | 0.2526 | 19819360 | WP_Hook->apply_filters( $value = '<!-- wp:paragraph -->\n<p><strong>NCERT solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 – Why Do We Fall Ill? (Updated)</strong></p>\n<!-- /wp:paragraph -->\n\n<!-- wp:table-of-contents-block/table-of-contents-block {"headers":[{"level":3,"content":"\\u003cstrong\\u003eNCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science – Page 178:\\u003c/strong\\u003e","text":"NCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science – Page 178:","link":"ncert-textbook-for-class-9-science-page-178"},{"level":3,"content":"In-Text Questions 13.2.5","text":"In-Text Questio'..., $args = [0 => '<!-- wp:paragraph -->\n<p><strong>NCERT solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 – Why Do We Fall Ill? (Updated)</strong></p>\n<!-- /wp:paragraph -->\n\n<!-- wp:table-of-contents-block/table-of-contents-block {"headers":[{"level":3,"content":"\\u003cstrong\\u003eNCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science – Page 178:\\u003c/strong\\u003e","text":"NCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science – Page 178:","link":"ncert-textbook-for-class-9-science-page-178"},{"level":3,"content":"In-Text Questions 13.2.5","text":"In-Text Questio'...] ) | .../plugin.php:205 |
| 13 | 0.2532 | 19820896 | do_blocks( $content = '<!-- wp:paragraph -->\n<p><strong>NCERT solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 – Why Do We Fall Ill? (Updated)</strong></p>\n<!-- /wp:paragraph -->\n\n<!-- wp:table-of-contents-block/table-of-contents-block {"headers":[{"level":3,"content":"\\u003cstrong\\u003eNCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science – Page 178:\\u003c/strong\\u003e","text":"NCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science – Page 178:","link":"ncert-textbook-for-class-9-science-page-178"},{"level":3,"content":"In-Text Questions 13.2.5","text":"In-Text Questio'... ) | .../class-wp-hook.php:324 |
| 14 | 0.2545 | 20125768 | render_block( $parsed_block = ['blockName' => 'table-of-contents-block/table-of-contents-block', 'attrs' => ['headers' => [...], 'title' => 'Chapter 13 – Why Do We Fall Ill?'], 'innerBlocks' => [], 'innerHTML' => '\n<div class="wp-block-table-of-contents-block-table-of-contents-block eb-toc-container" style="border:undefinedpx solid black;background:#fff6f3;box-shadow:0px 0px 0px 0px black;width:100%" data-collapsible="false" data-initial-collapse="false" data-scroll-top="false" data-sticky="false" data-text-color="#707070" data-hide-mobile="false" data-title-bg="#ff7d50" data-title-color="white"><div class="eb-toc-header"><div class="eb-toc-title" style="display:block;font-size:22px;font-weight:normal;letter-spacing:'..., 'innerContent' => [0 => '\n<div class="wp-block-table-of-contents-block-table-of-contents-block eb-toc-container" style="border:undefinedpx solid black;background:#fff6f3;box-shadow:0px 0px 0px 0px black;width:100%" data-collapsible="false" data-initial-collapse="false" data-scroll-top="false" data-sticky="false" data-text-color="#707070" data-hide-mobile="false" data-title-bg="#ff7d50" data-title-color="white"><div class="eb-toc-header"><div class="eb-toc-title" style="display:block;font-size:22px;font-weight:normal;letter-spacing:'...]] ) | .../blocks.php:1743 |
| 15 | 0.2546 | 20126368 | WP_Block->render( $options = ??? ) | .../blocks.php:1705 |
| 16 | 0.2546 | 20127064 | {closure:/home/kbxmjwdb/public_html/wp-content/plugins/table-of-contents-block/table-of-contents-block.php:116-270}( $attributes = ['headers' => [0 => [...], 1 => [...], 2 => [...], 3 => [...], 4 => [...], 5 => [...], 6 => [...], 7 => [...]], 'title' => 'Chapter 13 – Why Do We Fall Ill?'], $content = '\n<div class="wp-block-table-of-contents-block-table-of-contents-block eb-toc-container" style="border:undefinedpx solid black;background:#fff6f3;box-shadow:0px 0px 0px 0px black;width:100%" data-collapsible="false" data-initial-collapse="false" data-scroll-top="false" data-sticky="false" data-text-color="#707070" data-hide-mobile="false" data-title-bg="#ff7d50" data-title-color="white"><div class="eb-toc-header"><div class="eb-toc-title" style="display:block;font-size:22px;font-weight:normal;letter-spacing:'..., class WP_Block { public $parsed_block = ['blockName' => 'table-of-contents-block/table-of-contents-block', 'attrs' => [...], 'innerBlocks' => [...], 'innerHTML' => '\n<div class="wp-block-table-of-contents-block-table-of-contents-block eb-toc-container" style="border:undefinedpx solid black;background:#fff6f3;box-shadow:0px 0px 0px 0px black;width:100%" data-collapsible="false" data-initial-collapse="false" data-scroll-top="false" data-sticky="false" data-text-color="#707070" data-hide-mobile="false" data-title-bg="#ff7d50" data-title-color="white"><div class="eb-toc-header"><div class="eb-toc-title" style="display:block;font-size:22px;font-weight:normal;letter-spacing:'..., 'innerContent' => [...]]; public $name = 'table-of-contents-block/table-of-contents-block'; public $block_type = class WP_Block_Type { public $api_version = 2; public $name = 'table-of-contents-block/table-of-contents-block'; public $title = 'Table Of Contents'; public $category = 'widgets'; public $parent = NULL; public $ancestor = NULL; public $allowed_blocks = NULL; public $icon = NULL; public $description = 'Insert Table of Contents on your posts/pages and enhance user experience on your WordPress website'; public $keywords = [...]; public $textdomain = NULL; public $styles = [...]; private $variations = NULL; public $variation_callback = NULL; public $selectors = [...]; public $supports = [...]; public $example = NULL; public $render_callback = class Closure { virtual $closure = "{closure}", ... }; public $attributes = [...]; private $uses_context = [...]; public $provides_context = NULL; public $block_hooks = [...]; public $editor_script_handles = [...]; public $script_handles = [...]; public $view_script_handles = [...]; public $view_script_module_ids = [...]; public $editor_style_handles = [...]; public $style_handles = [...]; public $view_style_handles = [...]; private $deprecated_properties = [...] }; public $context = []; protected $available_context = ['postId' => 17685, 'postType' => 'post']; protected $registry = class WP_Block_Type_Registry { private $registered_block_types = [...] }; public $inner_blocks = []; public $inner_html = '\n<div class="wp-block-table-of-contents-block-table-of-contents-block eb-toc-container" style="border:undefinedpx solid black;background:#fff6f3;box-shadow:0px 0px 0px 0px black;width:100%" data-collapsible="false" data-initial-collapse="false" data-scroll-top="false" data-sticky="false" data-text-color="#707070" data-hide-mobile="false" data-title-bg="#ff7d50" data-title-color="white"><div class="eb-toc-header"><div class="eb-toc-title" style="display:block;font-size:22px;font-weight:normal;letter-spacing:'...; public $inner_content = [0 => '\n<div class="wp-block-table-of-contents-block-table-of-contents-block eb-toc-container" style="border:undefinedpx solid black;background:#fff6f3;box-shadow:0px 0px 0px 0px black;width:100%" data-collapsible="false" data-initial-collapse="false" data-scroll-top="false" data-sticky="false" data-text-color="#707070" data-hide-mobile="false" data-title-bg="#ff7d50" data-title-color="white"><div class="eb-toc-header"><div class="eb-toc-title" style="display:block;font-size:22px;font-weight:normal;letter-spacing:'...]; public $attributes = ['headers' => [...], 'title' => 'Chapter 13 – Why Do We Fall Ill?'] } ) | .../class-wp-block.php:463 |
NCERT solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 – Why Do We Fall Ill? (Updated)
List of subtopics covered in Chapter 13 – Why Do We Fall Ill?
| Number | Subtopic |
| 13.1 | Health and its failure |
| 13.1.1 | The significance of ‘Health’ |
| 13.1.2 | Personal and community issues both matter for health |
| 13.1.3 | The distinction between healthy and disease-free |
| 13.2 | Diseases and its causes |
| 13.2.1 | What does diseases look like? |
| 13.2.2 | Acute and chronic diseases |
| 13.2.3 | Chronic diseases and poor health |
| 13.2.4 | Causes of diseases |
| 13.2.5 | Infectious and non-infectious diseases |
| 13.3 | Infectious diseases |
| 13.3.1 | Infectious agents |
| 13.3.2 | Means of spread |
| 13.3.3 | Organ-specific and tissue-specific manifestations |
| 13.3.4 | Principles of treatment |
| 13.3.5 | Principles of prevention |
List of Exercise
Number 13.1 – 13.1.3 3 Question ( 3 short)
Number 13.1.4 -13.2.5 2 Question ( 2 short)
Number 13.3.5 5 Question ( 5 short)
Exercise Solutions 3 Question ( 2 long, 1 short)
Exercise Solutions 3 Question ( 1 long, 2 short)
NCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science – Page 178:
1. State any two conditions essential for good health.
Solution:
- Good economic condition and earnings
- Social environment
2. State any two conditions essential for being free of disease.
Solution:
- Living in a healthy and hygienic environment.
- Getting vaccination against infectious disease whenever required.
3. Are the answers to the above questions necessarily the same or different? Why?
Solution:
The answers to the above questions are different because a person may be free of disease but not be good mentally, socially and economically.
In-Text Questions 13.2.5
1. List any three reasons why you would think that you are sick and ought to see a doctor. If only one of these symptoms were present, would you still go to the doctor? Why or why not?
Solution:
(a). Headache, fever
(b). Muscle pain
(c). Dysentery
Usually, we do not visit a doctor if any one of the symptoms is observed as it does not affect the general health of the ability to work. But, if these symptoms are seen for a long period of time then we should consult a doctor for proper treatment.
2. In which of the following case do you think the long-term effects on your health are likely to be most unpleasant?
- if you get jaundice
- if you get lice
- if you get acne. Why?
Solution:
Jaundice causes a long term effect on our health. This chronic disease lasts for a long period of time. Jaundice develops slowly and does not spread rapidly.
In-Text Questions 13.3.5
1. Why are we normally advised to take bland and nourishing food when we are sick?
Solution:
When we fall sick, normal body functioning gets disturbed and do not function normally. As a result, improper digestion ability, we lose appetite and absorption of food is slow. Therefore, we are advised to take bland and nourishing food during sickness as it is easily digested and contains adequate nutrients, vitamins and minerals to produce energy.
2. What are the different means by which infectious diseases are spread?
Solution:
Infectious diseases are generally spread through the following modes – Water, air, vector such as mosquito, sexual contact, physical contact with the affected, or by using affected person’s clothes, bedding, utensils, etc.
3. What precautions can you take in your school to reduce the incidence of infectious diseases?
Solution:
Some of the precautions that we can take in our school to reduce the incidence of infectious diseases are –
(a). Trying to stay away from students who are infected.
(b). Covering mouth and nose while coughing and sneezing.
(c). Keeping the school environment clean so that there are no multiplication vectors.
(d). Consuming safe aqua guard water.
4. What is immunization?
Solution:
The method to boost our immune system with the help of vaccines that help the body to fight against infectious diseases is called immunization.
5. What are the immunization programs available at the nearest health center in your locality? Which of these diseases are the major health problems in your area?
Solution:
The immunization programs available at the nearest health centers are Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR), polio vaccine, jaundice, Diptheria, Pertusis, and Tetanus (DPT), typhoid, hepatitis B.
From above typhoid and jaundice create major health problems.
Exercise Questions
1. How many times did you fall ill in the last one year? What were the illnesses? (a). Think of one change you could make in your habits in order to avoid any of/most of the above illnesses.
(b). Think of one change you would wish for in your surroundings in order to avoid any of/most of the above illnesses.
Solution:
I fell ill twice in the last year. I suffered from diarrhea first and then dengue fever.
(a) The changes made by me in my habits after suffering from these diseases are –
(i) I will always drink purified and clean water and wash my hands before eating any food item.
(ii) I will live in a clean environment where disease spreading vectors will not multiply.
Example of multiplying vectors are mosquitoes.
(b) One change I would wish for in our surroundings in order to have a healthy society is by making pure drinking water available for the people. Consuming impure water is the root cause of many infectious diseases.
2. A doctor/nurse/health-worker is exposed to more sick people than others in the community. Find out how she/he avoids getting sick herself/himself.
Solution:
Some important precautions that need to be taken by the doctor/nurse/health-worker while treating people who are sicker than others in the community are –
(a). When in contact with a diseased person not to forget to wear a mask.
(b). Drinking purified water.
(c). Not neglecting cleanliness and personal hygiene.
(d). Keeping themselves covered appropriately when moving in an infected region
(e). Eating nutritious food and maintaining a healthy diet.
3. Conduct a survey in your neighborhood to find out what the three most common diseases are. Suggest three steps that could be taken by your local authorities to bring down the incidence of these diseases.
Solution:
The following three are the most common diseases in any neighborhood:
Cold and cough, loose motions, and malaria.
Some of the preventive measures that can be taken are:
(a). By drinking fresh, uncontaminated, and clean water.
(b). By maintaining hygienic sanitary conditions.
(c). By educating people about various preventive measures with the help of posters, and pamphlets.
Exercise Questions 188
4. A baby is not able to tell her/his caretakers that she/he is sick. What would help us to find out
(a) that the baby is sick?
(b) what is the sickness?
Solution:
(a). It can be found out by observing the behavioral changes of the child such as:
- Improper food intake
- Constant crying
- Mood changes frequently
(b). The sickness can be determined with the help of symptoms or indications shown by the child. The symptoms could be loose motion, vomiting, paleness in body and fever.
5. Under which of the following conditions is a person most likely to fall sick?
(a) when she is recovering from malaria.
(b) when she has recovered from malaria and is taking care of someone suffering from chicken-pox.
(c) when she is on a four-day fast after recovering from malaria and is taking care of someone suffering from chicken-pox. Why?
Solution:
A condition in which a person is most likely to fall sick when she is on a four-day fasting as soon as she has recovered from malaria and is taking care of someone suffering from chicken-pox. Because she has not completely recovered from malaria and she is fasting when her immune system is still weak. At this stage her body will not be able to fight against infection and if she is taking care of someone else suffering from chicken pox even she can get infected with chickenpox virus and will fall sick again.
Solutions for ncert Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Define health.
Answer. Health means a state of physical, mental and social well-being.
Question2. Define disease.
Answer: Disease means being uncomfortable.
Question 3. What do you mean by symptoms of disease?
Answer: Symptoms of disease are the signs of a disease which indicates the presence of a particular disease.
Question 4. What are acute diseases?
Answer: Those diseases which last for very short period of time are called acute diseases. Example, headache and cold.
Question 5. What are chronic diseases?
Answer: The diseases which last for very long period of time are called chronic disease Example, tuberculosis and jaundice.
Question 6. What are pathogens?
Answer: The disease causing microbes are called pathogens. Example, bacteria, virus, fungi, worms.
Question 7. What are vectors?
Answer: The organisms that spread or carry pathogens from one place to another, from infected person to healthy person is called vector.
Example, mosquito, housefly etc.
Question 8. What are infectious diseases?
Answer: Diseases which can spread from one person to another and microbes are the immediate cause for these diseases are called infectious diseases. Example, typhoid
Question 9. What are non-infectious diseases?
Answer: Diseases which do not spread from one person to another is called non-infectious diseases. Example, cancer.
Question 10. Name any one disease caused due to genetic abnormality.
Answer: Haemophilia.
Question 11. Name two diseases caused by protozoa.
Answer: Malaria and amoebiasis.
Question 12. Name two diseases caused due to bacteria.
Answer. Tuberculosis, typhoid.
Question 13. Name two disease caused due to virus.
Answer: Polio, chickenpox.
Question 14. Name two disease caused by fungi.
Answer: Scabies and skin infection.
Question 15. What are antibiotics?
Answer: Antibiotics are drugs that block the biochemical pathways important for bacteria. These are used to cure diseases caused due to bacteria.
Question 16. Give the full form of AIDS.
Answer: AIDS-Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome (Syndrome means collection of symptoms).
Question 17. Name the pathogen that causes sleeping sickness.
Answer: The protozoan → Trypanosoma.
Question 18. Name the organism that causes kala-azar.
Answer: Leishmania.
Question 19. Name two air-borne diseases.
Answer: Common cold, cough,* tuberculosis.
Question 20. Name two diseases that are organ specific.
Answer:
Jaundice – liver
Tuberculosis – lungs
Question 21. Which virus causes AIDS?
Answer: HIV virus causes AIDS
HIV—Human Immuno Deficiency Virus.
Solutions for Class 9 NCERT Science Chapter 13 Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Give the difference between acute disease and chronic disease.
Answer:
| Acute disease | Chronic disease |
| 1. It may last for few days.2. It does not have major effect on body. | 1. It lasts for longer period.2. It affects the body drastically. |
Question 2. State two main causes of disease.
Answer: Two main causes of disease are immediate cause and contributory cause. Immediate cause: This is due to the organisms that enter our body and cause disease. Example, virus, protozoa, bacteria.
Contributory cause: These are the secondary factors which lead these organisms to enter our body. Example, dirty water, unclean surrounding, contaminated food etc.
Question 3. Define vaccine and name two vaccines.
Answer: Vaccine is a chemical /drug given in advance to a body to give immunity against certain diseases.
Vaccines given to children are:
(a) BCG—for tuberculosis prevention
(b) Polio drops—for polio prevention
Question 4. What is antibiotic penicillin? Give its function.
Answer: Penicillin antibiotic blocks the bacterial processes that build the cell wall. Due to this drug, the bacteria is unable to make a protective cell wall and dies easily. It is used to cure the diseases and infections caused by bacteria.
Question 5. Bacteria is a cell, antibiotics can kill these bacteria (cell), Human body is also made of cells how does it affect our body?
Answer: Antibiotics block the biochemical pathway of bacteria by which it makes a protective cell wall around it. Antibiotic does not allow the bacteria to make this cell wall because of which they die.
Human body cell don’t make any cell wall so antibiotics cannot have any such effect on our body.
Question 6. How does cholera becomes an epidemic in a locality?
Answer: Cholera is an infectious disease that spreads due to unsafe water. It can spread in a locality; if a person suffering from cholera lives in the locality and
the excreta of this person, get mixed with the drinking water used by people living nearby. The cholera-causing microbe enters the new hosts through the water they drink and cause disease in them.
Question 7. Name the organs affected due to the following diseases:
Malaria, jaundice, Japanese encephalitis, typhoid.
Answer:
- Malaria: Infects liver and red blood cells
- Jaundice: Infects the liver.
- Japanese encephalitis: Infects the brain
- Typhoid: Infects blood.
Question 8. Why are sick patients advised to take bed rest?
Answer: Doctors advise to take bed rest for sick patients so that they can conserve their energy which can be used for healing of their body organs which were affected due to certain disease.
Question 9. How do we kiU microbes that enter our body and cause diseases?
Answer: Microbes can be killed by using medicines These microbes are of different categories—virus, bacteria, fungi or protoza. Each of these groups of organisms have some essential biochemical life processes which is peculiar to a particular group and is not shared by others. These pathways are not used by us. By using drugs that blocks the microbial synthesis pathway without affecting us can kill the microbes.
Question 10. What are disease specific means of prevention?
Answer: The disease specific means of prevention are the use of vaccines. The vaccines, are used against tetanus, diphtheria, whooping cough, measles, polio and many others.
Question 11. Why can’t we make antiviral medicines/drugs?
Answer: The viruses lie on the border line of living and non-living organisms. The viruses can live, grow and multiply only inside the host body. They cannot be grown or cultured and their .biological pathways cannot be affected. Hence, the antiviral medicines/drugs is difficult to make.
Question 12. Write a short note on malaria as a disease, its symptoms and control.
Answer: Malaria is caused by protozoa that lives in blood. This parasite enters our body through a female Anopheles mosquito bite which is the vector, visits water to lay eggs, the protozoa enters our blood stream when female mosquito bites us. This protozoa affects our liver and red blood cells.
Symptoms: Very high fever with periodic shivering, headache and muscular pain. –
Control: Use of quinine drug, keeping the surroundings clean with no stagnant water, use of mosquito repellent creams, nets, can control the spread of this disease.
Question 13. What is AIDS? How does a person get affected with HIV?
Answer: AIDS is Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome, it is caused due to HIV— human immuno deficiency virus. This virus reduces the immunity of human body. Therefore if any microbe enters the body of a person it causes disease killing the person.
The virus is transmitted from infected person to other person by any of the following way:
(a) Blood transfusion.
(b) From mother (infected) to baby in the womb.
(c) From mother’s milk to lactating baby.
(d) By sexual contact.
(e) Sharing of needle with an infected person.
Question 14. Becoming exposed to or infected with an infectious microbe does not necessarily mean developing noticeable disease. Explain.
Answer: This is because the immune system of our body is normally fighting off microbes. Our body have cells that are specialised in killing infecting microbes. Whenever any microbes or foreign body enters our system, these cells become active and kill the microbes that could cause any damage to the body. These immune cells manage to kill off the infection and a person does not get disease.
Question 15. What are three limitations for the approach to deal with infectious diseases?
Answer: The three limitations are:
(1) If someone has a disease, their body functions are damaged and may never recover completely.
(2) As the treatment will take time, the person suffering from a disease is likely to be bedridden for some time.
(3) The infectious person can serve as the source from where the infection may spread to other people.
Question 16. Give the common methods of transmission of diseases.
Answer: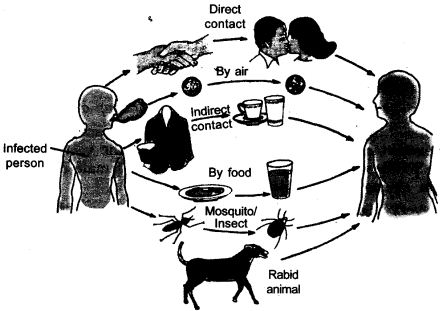
The common methods of transmission of diseases are:
(1) By air – cough, cold, tuberculosis
(2) By food and water – typhoid, jaundice
(3) By mosquito bite – malaria
(4) By rabid animal – rabies
(5) By direct contact – skin infection, small pox, AIDS
(6) By indirect contact – typhoid, chickenpox
Question 17. What are the basic conditions for good healths?
Answer: The basic conditions for good health are:
(1) Proper balanced and nutritious diet
(2) Personal hygiene
(3) Clean surroundings and clean environment
(4) Regular rest
(5) Proper rest
(6) Good economic status.
Solutions for NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. If someone in the family gets infectious disease, what precautions will you advice to the other family members?
Answer: For an infectious diseased person in the family following precautions should be taken:
(1) The surroundings and the house should be clean.
(2) The infected person should be kept isolated in a separate room.
(3) The clothes and utensils of patient should be sanitized regularly.
(4) Separate towels and handkerchief should be used by the patient.
(5) Children should not be allowed to visit the infected person.
(6) Clean and boiled drinking water should be given to the patient.
(7) A balanced and nutritious diet which will provide lot of energy should be given.
(8) There should be silence and the patient should be given lot of bedrest to overcome the infection.
Question 2. What is a disease? Classify disease based on duration and infection cause.
Answer: Disease can be defined as the state of human health which is not at ease is not comfortable. During disease, the functioning or appearance of one or more systems of the body changes.
Classification:
(a) Based on duration:
Acute diseases: Diseases that last for only short period of time. Example, headache, common cold etc.
Chronic diseases: Diseases that last for long time is called chronic disease Example, tuberculosis.
(b) Based on cause: Disease can be grouped as infectious/communicable disease and non-infectious or non-communicable disease.
Infectious diseases: These diseases are caused due to microbes and can spread from one person to another.
Non-infectious diseases: These type of diseases do not spread in the community, but remains internal. Example, cancer, genetic abnormalities.
Question 3. What are the different ways used for the treatment and prevention of diseases?
Answer: Principles of treatment for diseases are:
(1) To reduce the effect of the diseases.
(2) To kill the cause of the disease i.e., to kill the microbes like bacteria, fungi, protozoa.
Principles of prevention are:
(a) General ways: It relate to preventing exposure to the microbes. This can be done in following ways:
- For avoiding air-borne infections—Avoid visiting public place, cover your nose and mouth while sneezing or coughing
- For water-borne infection—Drink safe, clean and boiled water.
- For vector-borne diseases—Keep the surroundings clean, keep food and water covered and clean. Do not allow any water to stand as it becomes a breeding ground for mosquitoes.
- Self immunity—It is self-defence mechanism in our system that can fight off and kill microbes that enter our body.
(b) Specific ways—By giving vaccines, childhood immunisation that is given to children for preventing infections and diseases.
Question 4. State the mode of transmission for the following diseases:
Malaria, AIDS, Jaundice, Typhoid, Cholera, Rabies, Tuberculosis, Diarrhoea, Hepatitis, Influenza.
Answer:
| SL. No. | Diseases | Mode of transmission |
| 1. | Malaria | Mosquito bite (female Anopheles mosquito carries protozoa) |
| 2. | AIDS | Infected blood, semen, mother’s milk, from mother to foetus. |
| 3. | Jaundice | Contaminated water. |
| 4. | Typhoid | Contaminated food and water. |
| 5. | Cholera | Contaminated food and water. |
| 6. | Rabies | Bite of rabid animal. |
| 7. | Tuberculosis | Cough and sneeze droplets. |
| 8. | Diarrhoea | Contaminated food and water. |
| 9. | Hepatitis | Contaminated food and water. |
| 10. | Influenza | Cough and sneeze droplets. |
Question 5. Name all the micro-organisms that causes infectious disease and name few diseases caused by each micro-organism.
Answer:
| Infections Micro-organism | Disease |
| Bacteria | Tuberculosis, typhoid, diarrhoea, cholera |
| Virus | Polio, AIDS, chickenpox |
| Protozoa | Malaria, amoebiasis, kala-azar, sleeping sickness |
| Fungi | Food poisoning, skin diseases |








