(i) -2/3 × 3/5 + 5/2 – 3/5 × 1/6
-2/3 × 3/5 + 5/2 – 3/5 × 1/6
= -2/3 × 3/5– 3/5 × 1/6+ 5/2 (by commutativity)
= 3/5 (-2/3 – 1/6)+ 5/2
= 3/5 ((- 4 – 1)/6)+ 5/2
= 3/5 ((–5)/6)+ 5/2 (by distributivity)
= – 15 /30 + 5/2
= – 1 /2 + 5/2
= 4/2
= 2
(ii) 2/5 × (- 3/7) – 1/6 × 3/2 + 1/14 × 2/5
Solution:
= 2/5 × (- 3/7) + 1/14 × 2/5 – (1/6 × 3/2) (by commutativity)
= 2/5 × (- 3/7 + 1/14) – 3/12
= 2/5 × ((- 6 + 1)/14) – 3/12
= 2/5 × ((- 5)/14)) – 1/4
= (-10/70) – 1/4
= – 1/7 – 1/4
= (– 4– 7)/28
= – 11/28
2. Write the additive inverse of each of the following
Solution:
(i) 2/8
Additive inverse of 2/8 is – 2/8
(ii) -5/9
Additive inverse of -5/9 is 5/9
(iii) -6/-5 = 6/5
Additive inverse of 6/5 is -6/5
(iv) 2/-9 = -2/9
Additive inverse of -2/9 is 2/9
(v) 19/-16 = -19/16
Additive inverse of -19/16 is 19/16
3. Verify that: -(-x) = x for.
(i) x = 11/15
(ii) x = -13/17
Solution:
(i) x = 11/15
We have, x = 11/15
The additive inverse of x is – x (as x + (-x) = 0)
Then, the additive inverse of 11/15 is – 11/15 (as 11/15 + (-11/15) = 0)
The same equality 11/15 + (-11/15) = 0, shows that the additive inverse of -11/15 is 11/15.
Or, – (-11/15) = 11/15
i.e., -(-x) = x
(ii) -13/17
We have, x = -13/17
The additive inverse of x is – x (as x + (-x) = 0)
Then, the additive inverse of -13/17 is 13/17 (as 13/17 + (-13/17) = 0)
The same equality (-13/17 + 13/17) = 0, shows that the additive inverse of 13/17 is -13/17.
Or, – (13/17) = -13/17,
i.e., -(-x) = x
4. Find the multiplicative inverse of the
(i) -13 (ii) -13/19 (iii) 1/5 (iv) -5/8 × (-3/7) (v) -1 × (-2/5) (vi) -1
Solution:
(i) -13
Multiplicative inverse of -13 is -1/13
(ii) -13/19
Multiplicative inverse of -13/19 is -19/13
(iii) 1/5
Multiplicative inverse of 1/5 is 5
(iv) -5/8 × (-3/7) = 15/56
Multiplicative inverse of 15/56 is 56/15
(v) -1 × (-2/5) = 2/5
Multiplicative inverse of 2/5 is 5/2
(vi) -1
Multiplicative inverse of -1 is -1
5. Name the property under multiplication used in each of the following.
(i) -4/5 × 1 = 1 × (-4/5) = -4/5
(ii) -13/17 × (-2/7) = -2/7 × (-13/17)
(iii) -19/29 × 29/-19 = 1
Solution:
(i) -4/5 × 1 = 1 × (-4/5) = -4/5
Here 1 is the multiplicative identity.
(ii) -13/17 × (-2/7) = -2/7 × (-13/17)
The property of commutativity is used in the equation
(iii) -19/29 × 29/-19 = 1
Multiplicative inverse is the property used in this equation.
6. Multiply 6/13 by the reciprocal of -7/16
Solution:
Reciprocal of -7/16 = 16/-7 = -16/7
According to the question,
6/13 × (Reciprocal of -7/16)
6/13 × (-16/7) = -96/91
7. Tell what property allows you to compute 1/3 × (6 × 4/3) as (1/3 × 6) × 4/3
Solution:
1/3 × (6 × 4/3) = (1/3 × 6) × 4/3
Here, the way in which factors are grouped in a multiplication problem, supposedly, does not change the product. Hence, the Associativity Property is used here.
8. Is 8/9 the multiplication inverse of
–
Solution:
According to the question,
8/9 × (-7/8) = -7/9 ≠ 1
Therefore, 8/9 is not the multiplicative inverse of
9. If 0.3 the multiplicative inverse of
Solution:
0.3 = 3/10[Multiplicative inverse ⟹ product should be 1]
According to the question,
3/10 × 10/3 = 1
Therefore, 0.3 is the multiplicative inverse of
10. Write
(i) The rational number that does not have a reciprocal.
(ii) The rational numbers that are equal to their reciprocals.
(iii) The rational number that is equal to its negative.
Solution:
(i)The rational number that does not have a reciprocal is 0. Reason:
0 = 0/1
Reciprocal of 0 = 1/0, which is not defined.
(ii) The rational numbers that are equal to their reciprocals are 1 and -1.
Reason:
1 = 1/1
Reciprocal of 1 = 1/1 = 1 Similarly, Reciprocal of -1 = – 1
(iii) The rational number that is equal to its negative is 0.
Reason:
Negative of 0=-0=0
11. Fill in the blanks.
(i) Zero has _______reciprocal.
(ii) The numbers ______and _______are their own reciprocals
(iii) The reciprocal of – 5 is ________.
(iv) Reciprocal of 1/x, where x ≠ 0 is _________.
(v) The product of two rational numbers is always a ________.
(vi) The reciprocal of a positive rational number is _________.
Solution:
(i) Zero has no reciprocal.
(ii) The numbers -1 and 1 are their own reciprocals
(iii) The reciprocal of – 5 is -1/5.
(iv) Reciprocal of 1/x, where x ≠ 0 is x.
(v) The product of two rational numbers is always a rational number.
(vi) The reciprocal of a positive rational number is positive.
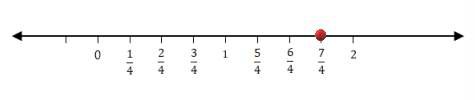
1. Represent these numbers on the number line.
(i) 7/4
(ii) -5/6
Solution:
(i) 7/4
Divide the line between the whole numbers into 4 parts. i.e., divide the line between 0 and 1 to 4 parts, 1 and 2 to 4 parts and so on.
Thus, the rational number 7/4 lies at a distance of 7 points away from 0 towards positive number line.
(ii) -5/6
Divide the line between the integers into 4 parts. i.e., divide the line between 0 and -1 to 6 parts, -1 and -2 to 6 parts and so on. Here since the numerator is less than denominator, dividing 0 to – 1 into 6 part is sufficient.
Thus, the rational number -5/6 lies at a distance of 5 points, away from 0, towards negative number line
2. Represent -2/11, -5/11, -9/11 on a number line.
Solution:
Divide the line between the integers into 11 parts.
Thus, the rational numbers -2/11, -5/11, -9/11 lies at a distance of 2, 5, 9 points away from 0, towards negative number line respectively.
3. Write five rational numbers which are smaller than 2.
Solution:
The number 2 can be written as 20/10
Hence, we can say that, the five rational numbers which are smaller than 2 are:
2/10, 5/10, 10/10, 15/10, 19/10
4. Find the rational numbers between -2/5 and ½.
Solution:
Let us make the denominators same, say 50.
-2/5 = (-2 × 10)/(5 × 10) = -20/50
½ = (1 × 25)/(2 × 25) = 25/50
Ten rational numbers between -2/5 and ½ = ten rational numbers between -20/50 and 25/50
Therefore, ten rational numbers between -20/50 and 25/50 = -18/50, -15/50, -5/50, -2/50, 4/50, 5/50, 8/50, 12/50, 15/50, 20/50
5. Find five rational numbers between.
(i) 2/3 and 4/5
(ii) -3/2 and 5/3
(iii) ¼ and ½
Solution:
(i) 2/3 and 4/5
Let us make the denominators same, say 60
i.e., 2/3 and 4/5 can be written as:
2/3 = (2 × 20)/(3 × 20) = 40/60
4/5 = (4 × 12)/(5 × 12) = 48/60
Five rational numbers between 2/3 and 4/5 = five rational numbers between 40/60 and 48/60
Therefore, Five rational numbers between 40/60 and 48/60 = 41/60, 42/60, 43/60, 44/60, 45/60
(ii) -3/2 and 5/3
Let us make the denominators same, say 6
i.e., -3/2 and 5/3 can be written as:
-3/2 = (-3 × 3)/(2× 3) = -9/6
5/3 = (5 × 2)/(3 × 2) = 10/6
Five rational numbers between -3/2 and 5/3 = five rational numbers between -9/6 and 10/6
Therefore, Five rational numbers between -9/6 and 10/6 = -1/6, 2/6, 3/6, 4/6, 5/6
(iii) ¼ and ½
Let us make the denominators same, say 24.
i.e., ¼ and ½ can be written as:
¼ = (1 × 6)/(4 × 6) = 6/24
½ = (1 × 12)/(2 × 12) = 12/24
Five rational numbers between ¼ and ½ = five rational numbers between 6/24 and 12/24
Therefore, Five rational numbers between 6/24 and 12/24 = 7/24, 8/24, 9/24, 10/24, 11/24
6. Write five rational numbers greater than -2.
Solution:
-2 can be written as – 20/10
Hence, we can say that, the five rational numbers greater than -2 are
-10/10, -5/10, -1/10, 5/10, 7/10
7. Find ten rational numbers between 3/5 and ¾,
Solution:
Let us make the denominators same, say 80.
3/5 = (3 × 16)/(5× 16) = 48/80
3/4 = (3 × 20)/(4 × 20) = 60/80
Ten rational numbers between 3/5 and ¾ = ten rational numbers between 48/80 and 60/80
Therefore, ten rational numbers between 48/80 and 60/80 = 49/80, 50/80, 51/80, 52/80, 54/80, 55/80, 56/80, 57/80, 58/80, 59/80
Hemchandracharya North Gujarat University (HNGU) has announced the results for various UG and PG courses,…
Are you interested in learning about the Indian Army Ordnance Corps (AOC) Salary, Allowances, and…
RMLAU Result 2024 Declared: Check UG and PG Odd Semester Results at rmlau.ac.in The Dr.…
Rupal Rana's achievement of securing All India Rank 26 in the UPSC exams is not…
UPSC Calendar 2025 Released at upsc.gov.in: Check CSE, NDA, CDS, and Other Exam Notification, Application,…
JSSC Teacher Admit Card 2024 Released at jssc.nic.in: Download JPSTAACCE Call Letter Here The Jharkhand…